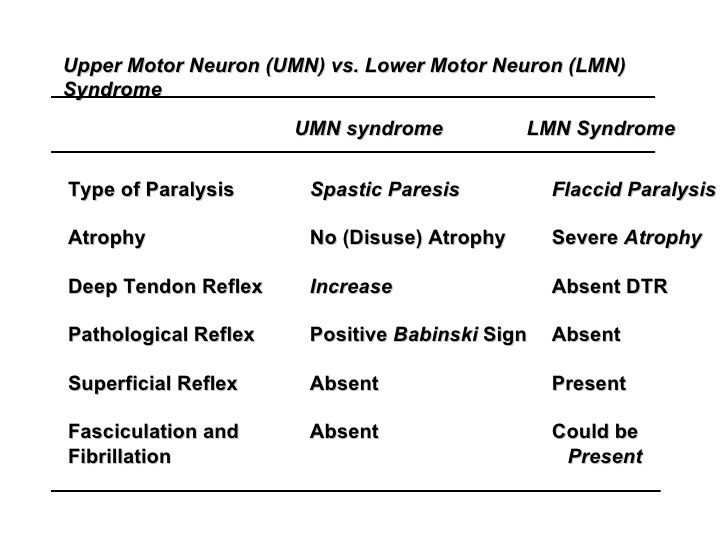
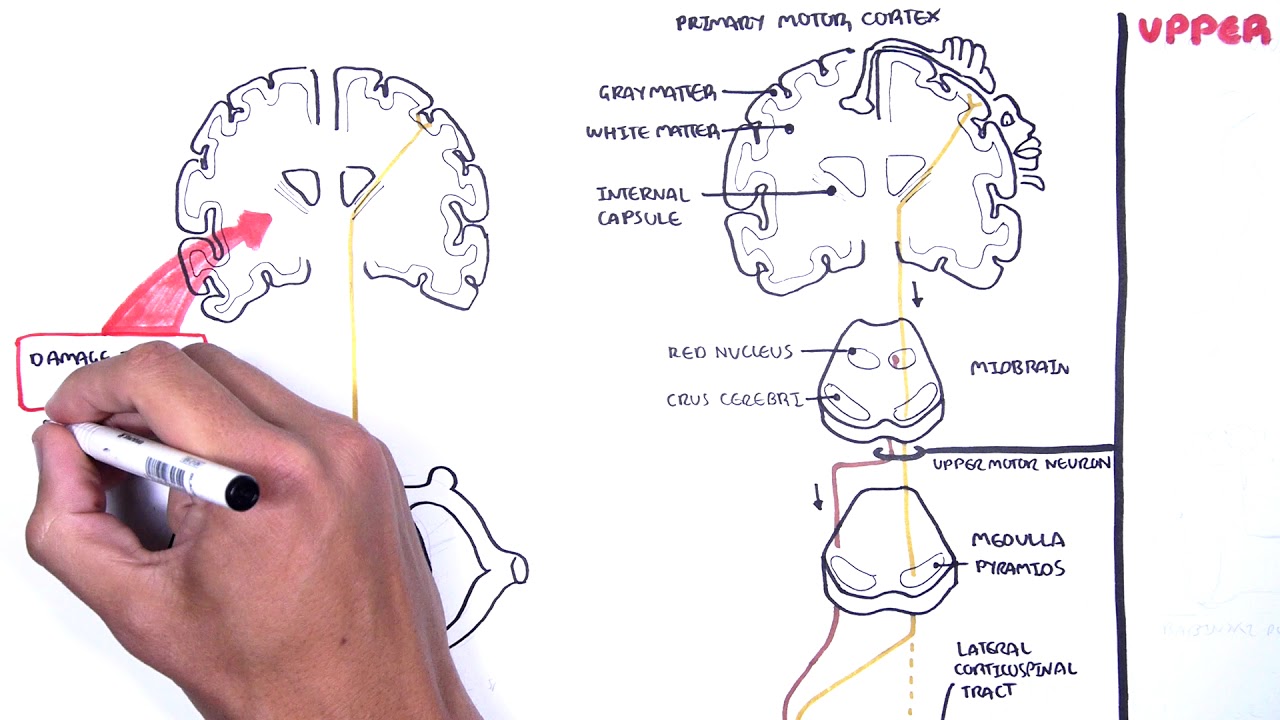
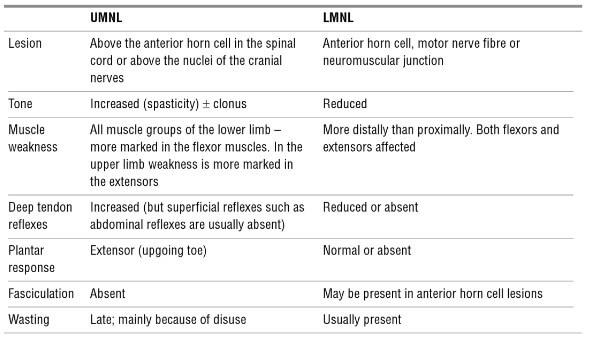
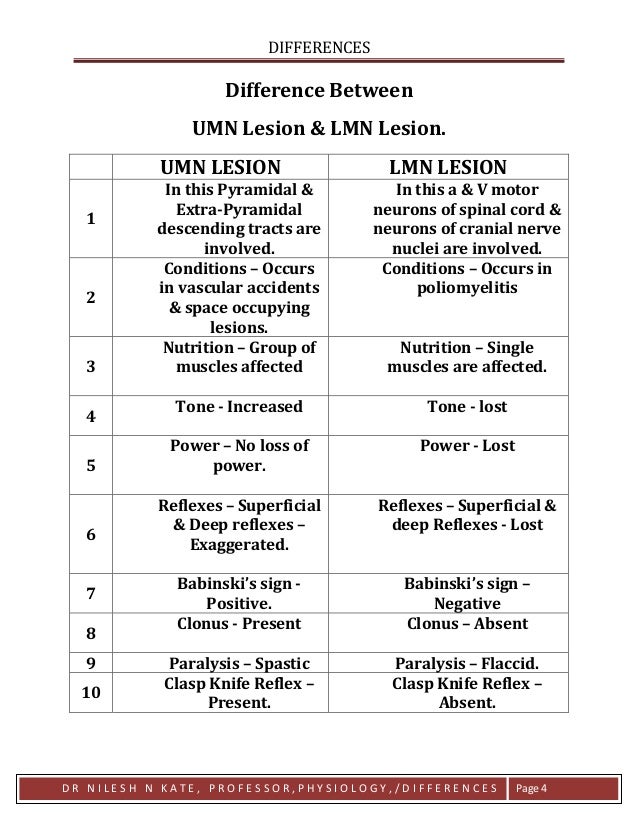
Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Vs Lower Motor Neuron Lesion Symptoms

A lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord to the associated muscle s.
Upper motor neuron lesion vs lower motor neuron lesion symptoms. Fibrosis and atrophy 3. Http bit ly ptmsk download our app. Stroke or spinal cord injury. Https goo gl 3nkzjx get our assessment b.
Lower motor neuron pathology. Upper motor neuron findings include. Enroll in our online course. Spasticity is part of the positive signs among other motor symptoms which occur after lesions in the descending corticospinal system such as spastic dystonia muscle constriction in the absence of.
Decreased muscle tone with absent or diminished lower extremity weakness on the affected side are usually seen in lumbosacral plexus injury lower motor neuron signs. Tone remains increased regardless of how quickly the joint is moved. One major characteristic used to identify a lower motor neuron lesion is flaccid paralysis paralysis accompanied by loss of muscle tone. This is the typical finding with an upper motor neuron lesion e g.
Distribution distal proximal. A neurologic examination should be performed in patients with muscle weakness to observe signs of upper motor neuron vs. An upper motor neuron lesion is a lesion of the neural pathway above the anterior horn of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other motor neuron diseases are characterized by steady relentless progressive degeneration of corticospinal tracts anterior horn cells bulbar motor nuclei or a combination.
A lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the lower motor neuron s in the anterior horn anterior grey column of the spinal cord or in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves to the relevant muscle s. The upper motor neuron syndrome can be defined by positive and negative signs 2. Either may be more prominent asymmetric often involves paraspinous respiratory muscles often spares bulbar musculature spontaneous motor activity cramps. One example of this is parkinson s disease where limb movement generates a ratchet like sensation known as cog wheeling.
Vs 55 in als. Symptoms vary in severity and may include muscle weakness and atrophy fasciculations. If the lumbar plexus is involved the patellar reflex is usually diminished whereas if the sacral portion of the plexus is involved the hamstrings and achilles reflexes can be.